In this tutorial, we'll explain how to scrape Crunchbase - the most extensive public resource for financial information of various public and private companies and investments.
Crunchbase contains thousands of company profiles, which include investment data, funding information, leadership positions, mergers, news and industry trends.
To scrape Crunchbase, we'll be using the hidden web data web scraping approach using Python with an HTTP client library.
Mostly, we'll focus on capturing company data through generic scraping techinques we'll learn, which can be easily applied to other Crunchbase areas such as people or acquisition data with a minimum effort. Let's dive in!
Key Takeaways
Master crunchbase api scraping with advanced Python techniques, business data extraction, and company monitoring for comprehensive startup and investment analysis.
- Reverse engineer Crunchbase's API endpoints by intercepting browser network requests and analyzing JSON responses
- Extract structured business data including funding details, company information, and leadership profiles from startup directory
- Implement pagination handling and search parameter management for comprehensive business data collection
- Configure proxy rotation and fingerprint management to avoid detection and rate limiting
- Use specialized tools like ScrapFly for automated Crunchbase scraping with anti-blocking features
- Implement data validation and error handling for reliable business information extraction
Latest Crunchbase.com Scraper Code
Why Scrape Crunchbase.com?
Crunchbase has an enormous business dataset that can be used in various forms of market analytics and business intelligence research. For example, the company dataset contains the company's summary details (like description, website and address), public financial information (like acquisitions and investments) and used technology data.
Additionally, Crunchbase data contains many data points used in lead generation, like the company's contact details, leadership's social profiles, and event aggregation.
For more on scraping use cases see our extensive web scraping use case article.
Project Setup
To scrape Crunchbase, we'll be using Python with Scrapfly's Python SDK.
Additionally, we'll be using JMESPath Python library to refine large JSON documents we'll be scraping.
The above packages can be easily installed using the below pip command:
$ pip install scrapfly-sdk jmespath
Available Crunchbase Targets
Crunchbase contains several data types: acquisitions, people, events, hubs and funding rounds. Our Crunchbase scraper will focus on the company and people data. That being said, the same techincal concepts can be applied to other pages on Crunchbase.
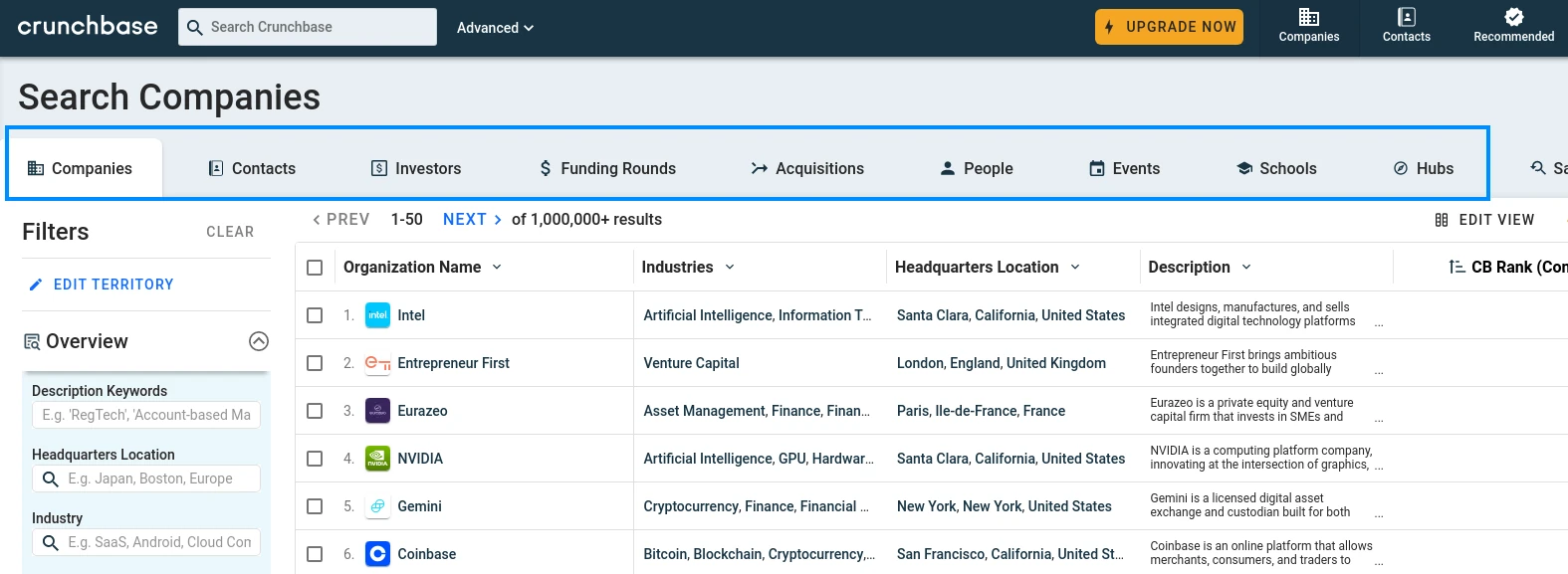
You can explore available data types by taking a look at the Crunchbase discovery pages.
Scraping Crunchbase Companies
The Crunchbase company page contains various data spread across multiple pages:
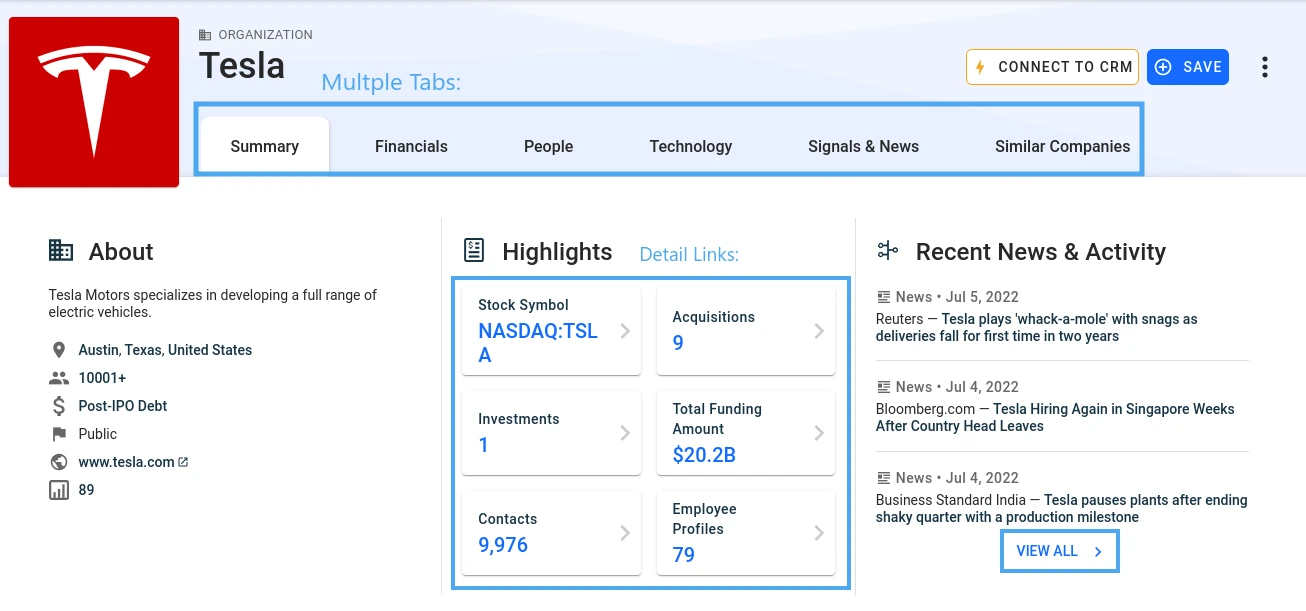
However, instead of parsing the HTML we can dig into the page source and we can see that the same data is also available in the page's app state variable:

We can see that a <script id="client-app-state"> node contains a large JSON file with a lot of the same details we see on the page. Since Crunchbase is using the Angular JavaScript front-end framework, it stores the HTML data in page state cache , which we can extract directly instead of parsing the HTML page. Let's take a look at how we can apply that:
Above we define our company scraper which as you can see is mostly parsing code. Let's quickly unpack our process here:
- We retrieve organizations' "people" tab page e.g. /tesla-motors/people. We use this page because all of the organization sub-pages (aka tabs) contain the same cache except the people's page in addition also contains some employee data.
- We find cache data in
<script id="app-state-data">and unquote it as it uses a special Angular quotation. - Load that us as JSON to Python's dictionary and select a few important fields from the dataset. Note, there's a lot of data in the cache - most of what's visible on the page and more - but for this demonstration, we stick to a few essential fields.
- We use
jmespathto refine the large JSON document retrieved for the important company data only.
Below is example output of the scraped Curnchbase company data:
Example output:
{
"organization": {
"name": "Tesla",
"id": "tesla-motors",
"logo": "https://res.cloudinary.com/crunchbase-production/image/upload/v1459804290/mkxozts4fsvkj73azuls.png",
"description": "Tesla Motors specializes in developing a full range of electric vehicles.",
"semrush_global_rank": 3462,
"semrush_visits_latest_month": 34638116
},
"employees": [
{
"name": "Kenneth Rogers",
"linkedin": "kenneth-rogers-07a7b149",
"job_levels": [
"l_500_exec"
],
"job_departments": [
"management"
]
},
...
]
}
As you can see, since we're scraping Angular cache directly instead of parsing HTML we can easily pick up the entire dataset in just a few lines of code! Can we apply this to scraping other data types hosted on Crunchbase?
Scraping Other Crunchbase Data Types
Crunchbase contains details not only of companies but of industry news, investors (people), funding rounds and acquisitions. Because we chose to approach parsing through Angular cache rather than HTML itself we can easily adapt our parser to extract data set from these other endpoints as well:
The example above uses the same technique we used to scrape company data to scrape investor data. By extracting data from Angular app state we can scrape the dataset of any Crunchbase endpoint with just a few lines of code!
Below is an example output of the data retrieved:
Example output:
{
"name": "Elon Musk",
"title": "Elon Musk - CEO @ Tesla",
"description": "Elon Musk has co-founded numerous companies including space exploration company SpaceX, brain-implant startup Neuralink, and tunneling start...",
"type": "investor",
"gender": "male",
"location_groups": [
"Greater Los Angeles Area",
"West Coast",
"Western US"
],
"location": [
"Los Angeles",
"California",
"United States",
"North America"
],
"current_jobs": 7,
"past_jobs": 5,
"education": [
{
"school": "University of Pennsylvania",
"type": "BA"
},
....
],
"timeline": [
"SpaceX IPO At $1.5T Valuation Would Be 10x Larger Than Biggest VC-Backed Listing Of All Time",
.....
],
"investments": [
{
"identifier": {
"uuid": "b0f10d18-c1d5-4620-9609-1a356606cba9",
"value": "Elon Musk investment in Venture Round - X (formerly Twitter)",
"permalink": "elon-musk-invested-in-twitter-series-unknown--636b0eaa--b0f10d18",
"entity_def_id": "investment"
},
....
},
....
],
"exits": [
{
"name": "X (formerly Twitter)",
"short_description": "X is a social networking platform that allows its users to send and read microblogs."
},
....
],
"investing_overview": {
"num_current_advisor_jobs": 8,
"num_founded_organizations": 7,
"preview_properties": {
"num_exits": {
"is_present": true
}
},
"num_portfolio_organizations": 4,
"rank_principal_investor": 24962
},
"linkedin": "https://www.linkedin.com/in/elon-m-346799137",
"twitter": "https://x.com/elonmusk",
"facebook": null,
"current_advisor_jobs": 8,
"founded_orgs": 7,
"portfolio_orgs": 4,
"rank_principal_investor": 24962
}
Bypass Blocking with ScrapFly
We looked at how to Scrape Crunchbase.com. However, when scraping at scale we are likely to be either blocked or start serving captchas to solve. This will hinder or completely disable our web scraper.
ScrapFly provides web scraping, screenshot, and extraction APIs for data collection at scale.
- Anti-bot protection bypass - scrape web pages without blocking!
- Rotating residential proxies - prevent IP address and geographic blocks.
- JavaScript rendering - scrape dynamic web pages through cloud browsers.
- Full browser automation - control browsers to scroll, input and click on objects.
- Format conversion - scrape as HTML, JSON, Text, or Markdown.
- Python and Typescript SDKs, as well as Scrapy and no-code tool integrations.
For more, explore web scraping API and its documentation.
To scrape Crunchbase with scrapfly-sdk we can start by installing scrapfly-sdk package using pip:
$ pip install scrapfly-sdk
To take advantage of ScrapFly's API in our Crunchbase scraper, all we need to do is change our httpx session code with scrapfly-sdk client requests. For avoiding Crunchbase scraping blocking, we'll use the anti scraping protection bypass feature, which can be enabled using asp=True argument. For example, let's take a look how can we use ScrapFly to scrape a single company page:
from scrapfly import ScrapflyClient, ScrapeConfig
client = ScrapflyClient(key='YOUR_SCRAPFLY_KEY')
result = client.scrape(ScrapeConfig(
url="https://www.crunchbase.com/organization/tesla-motors/people",
# we need to enable Anti Scraping Protection bypass with a keyword argument:
asp=True,
))
FAQ
To wrap this guide up let's take a look at some frequently asked questions about web scraping Crunchbase:
Is it legal to scrape Crunchbase.com ?
Yes. Crunchbase data is publicly available, and we're not extracting anything private. Scraping Crunchbase.com at slow, respectful rates would fall under the ethical scraping definition. That being said, attention should be paid to GDRP compliance in the EU when scraping personal data such as people's (investor) data. For more, see our Is Web Scraping Legal? article.
Can you crawl Crunchbase.com?
Yes, there are many ways to crawl crunchbase. The easiest way to retrieve the page URLs, and then extract their data using the snippets we wrote in this guide. For more, refer to our guide on crawling URLs from a domain.
Summary
In this tutorial, we built a Crunchbase scraper. We've taken a look at how to discover the company and people pages through Crunchbase's sitemap functionality. Then, we wrote a generic dataset parser for Angular-powered websites like Crunchbase itself and put it to use for scraping company and people data.
For this, we used Python, and to prevent being blocked we used ScrapFly's API which smartly configures every web scraper connection to avoid being blocked. For more on ScrapFly see our documentation and try it out for free!
Legal Disclaimer and Precautions
This tutorial covers popular web scraping techniques for education. Interacting with public servers requires diligence and respect and here's a good summary of what not to do:- Do not scrape at rates that could damage the website.
- Do not scrape data that's not available publicly.
- Do not store PII of EU citizens who are protected by GDPR.
- Do not repurpose the entire public datasets which can be illegal in some countries.