If you've ever encountered a message stating, "Web server is returning an unknown error (error code 520)," you're not alone. This common issue, often associated with Cloudflare, can disrupt online activities, leaving users seeking for solutions.
In this article, we'll explore what is error code 520, its causes, and actionable strategies to address and reduce it effectively.
Key Takeaways
Resolve error code 520 by implementing retry logic, configuring server settings, and handling Cloudflare communication issues. Learn to diagnose server-side problems and implement proper error handling for web scraping applications.
- Implement exponential backoff retry logic with 503 status code detection for temporary service unavailability
- Configure load balancing and connection pooling to distribute requests and avoid server overload
- Monitor server health and implement circuit breaker patterns for handling service downtime
- Use proxy rotation and IP address distribution to bypass server-side blocking and rate limiting
- Use specialized tools like ScrapFly for automated 503 error handling with anti-blocking features
- Implement graceful error handling and fallback mechanisms for service unavailability scenarios
What is Error Code 520 ?
Error code 520 is a generic response returned by Cloudflare when the web server fails to fulfill a request. To understand this, it's important to know how Cloudflare operates.
Cloudflare sits between the client (browser or app) and the origin server, acting as a proxy to improve performance, security, and reliability. When a user’s request reaches Cloudflare, it forwards the request to the origin server.
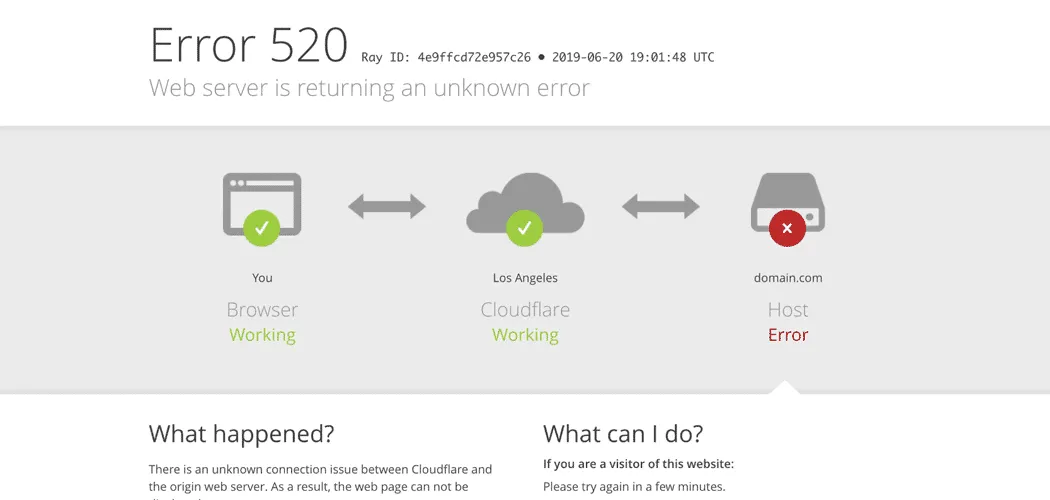
This error typically stems from the server-side, not Cloudflare itself, making troubleshooting dependent on investigating the origin server's configuration and responses.
Common Causes of Error Code 520
Understanding the root causes is essential to diagnosing and fixing the problem. Here’s a breakdown of the most frequent causes of error code 520:
Server Issues with Cloudflare
- Miscommunication between the origin server and Cloudflare is one of the primary culprits.
- Cloudflare acts as an intermediary, and if the server unexpectedly closes the connection or refuses it, Cloudflare returns a 520 error.
How to Fix It:
- For Server Admins: Ensure your server is configured to accept connections from Cloudflare. Check your firewall settings and whitelist Cloudflare's IP ranges. Additionally, verify that your server's resources are not being overwhelmed and that it can handle the traffic routed through Cloudflare.
- For Clients: If you encounter this error, contact the server administrator or the website owner. Let them know about the issue and suggest they review their server’s compatibility with Cloudflare's requests.
Empty Responses from the Server
- This occurs when the origin server fails to send any data in response to a request.
- An empty response could result from crashes, poorly written application code, or overloaded servers.
How to Fix It:
- For Server Admins: Check server logs for errors during the time of the failure. Inspect application code for bugs or crashes, and ensure the server has sufficient resources (CPU, memory) to handle the load. Consider setting up monitoring tools to detect and resolve these issues proactively.
- For Clients: Report the issue to the server administrator. Let them know you encountered a 520 error, and request they investigate server-side performance and stability.
Oversized HTTP Headers
- Cloudflare enforces a strict limit for HTTP headers (including cookies). If the server exceeds this size, Cloudflare triggers a 520 error.
- Headers that include excessive cookies or large custom data can be common causes.
How to Fix It:
- For Server Admins: Review and trim HTTP headers to ensure they don’t exceed Cloudflare’s 16KB limit. Remove unnecessary cookies, debugging data, or any large custom headers. Use tools like browser developer tools or cURL to inspect header sizes.
- For Clients: Clear your browser cookies and cache, as oversized cookies from prior sessions might contribute to the problem. If the issue persists, contact the website administrator.
Bad Server Configuration
- Misconfigured servers often fail to meet Cloudflare's expectations during requests.
- Issues like incorrect SSL settings, outdated software, or firewall rules blocking Cloudflare's IPs can lead to 520 errors.
How to Fix It:
- For Server Admins: Verify that your server has the correct SSL configuration and is using up-to-date software. Double-check that firewall settings allow Cloudflare’s IP ranges. Use Cloudflare’s diagnostic tools to identify and resolve configuration issues.
- For Clients: Inform the website owner about the issue, mentioning that misconfigured server settings might be the cause. Suggest they review their setup with Cloudflare’s guidelines.
Examples of Real-World Scenarios
Here are some practical examples of situations that trigger error code 520 cloudflare:
1. Oversized Headers Issue
A web developer adds unnecessary data to HTTP headers for debugging purposes, pushing the total size beyond the limit. As a result, Cloudflare blocks the request and returns an error.
2. Empty Response Due to Application Error
A poorly coded web application crashes under heavy load, failing to generate a response. Cloudflare, receiving no data, returns a 520 error to the user.
3. Miscommunication with the Server
A server is configured to close idle connections prematurely. When Cloudflare attempts to establish a connection, it’s terminated unexpectedly, resulting in a 520 error.
4. Blocked Cloudflare IPs
The origin server’s firewall is set to block Cloudflare IP ranges, mistakenly identifying them as malicious traffic. This misconfiguration prevents communication between Cloudflare and the server.
By understanding these root causes, webmasters can pinpoint the source of the problem and implement the necessary fixes to minimize disruptions.
How to Retry and Wait for 520 to Recover
Error 520 can sometimes resolve itself after a short interval, making retries an effective first step. Here are strategies to handle error code 520:
Retry Strategies
Retrying a failed request is often the quickest way to handle a 520 error code. Whether manually refreshing the page or implementing automated retries, giving the server time to recover can resolve the error without additional intervention.
1. Manual Refresh
The most basic method is manually reloading the webpage or resubmitting the request:
- Press the refresh button in your browser or use the shortcut
Ctrl + R(Windows) orCmd + R(Mac). - Wait a few seconds before retrying, especially during server traffic spikes.
This strategy works well for end users or casual browsing, but it’s not practical for automated systems or repetitive tasks.
2. Automated Retries
Automated retry mechanisms are useful when handling multiple requests or running critical systems that can’t rely on manual intervention. Below are various methods to automate retries in different programming languages and tools.
Retry Using cURL
cURL provides options to retry failed requests automatically:
curl --retry 5 --retry-delay 2 --retry-connrefused https://httpbin.dev
Explanation:
--retry 5: Retry up to 5 times.--retry-delay 2: Wait 2 seconds between retries.--retry-connrefused: Retry on connection refusals.
Retry Using Python and the requests Library
With Python’s requests library, you can automate retries using a loop and delays:
import requests
from time import sleep
url = "https://httpbin.dev"
for attempt in range(5):
try:
response = requests.get(url)
if response.status_code == 200:
print("Success!")
break
except requests.exceptions.RequestException:
print("Retrying...")
sleep(2) # Wait before retrying
This handles transient 520 errors while allowing time for server recovery.
Retry Using JavaScript and Axios
JavaScript developers can use Axios with a retry mechanism:
const axios = require("axios");
const retryRequest = async (url, retries, delay) => {
for (let attempt = 0; attempt < retries; attempt++) {
try {
const response = await axios.get(url);
console.log("Success:", response.data);
return;
} catch (error) {
console.log(`Attempt ${attempt + 1} failed. Retrying in ${delay}ms...`);
await new Promise((res) => setTimeout(res, delay));
}
}
console.log("All retries failed.");
};
retryRequest("https://httpbin.dev", 5, 2000);
Explanation:
- Retries are handled in a loop with delays using
setTimeoutvia aPromise.
Retry Using Go
In Go, you can implement retries using a loop with time.Sleep:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
"time"
)
func main() {
url := "https://httpbin.dev"
retries := 5
delay := 2 * time.Second
for attempt := 1; attempt <= retries; attempt++ {
resp, err := http.Get(url)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Attempt %d failed: %v\n", attempt, err)
time.Sleep(delay)
continue
}
body, _ := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
fmt.Println("Success:", string(body))
resp.Body.Close()
break
}
}
Explanation:
- The loop retries the request up to the defined number of times, with a delay between each attempt.
Retry Using Java with Apache HttpClient
Java developers can use Apache HttpClient for retries:
import org.apache.hc.client5.http.HttpResponseException;
import org.apache.hc.client5.http.fluent.Request;
public class RetryExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "https://httpbin.dev";
int retries = 5;
int delay = 2000; // in milliseconds
for (int attempt = 1; attempt <= retries; attempt++) {
try {
String response = Request.Get(url).execute().returnContent().asString();
System.out.println("Success: " + response);
break;
} catch (HttpResponseException e) {
System.out.println("Attempt " + attempt + " failed. Retrying...");
try {
Thread.sleep(delay);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
break;
}
}
}
}
Explanation:
- Handles retries in a loop, using
Thread.sleepfor delay between attempts.
Mitigating Error Code 520
Mitigating error code 520 can be challenging since it typically stems from server-side issues beyond the user's direct control. However, there are several strategies to minimize its impact and access essential data when errors occur.
Verify and Optimize Server Configuration
The most effective way to prevent future 520 errors is to address the root cause in the server setup. Key actions include:
Review DNS Settings:
Ensure DNS records are correctly configured for Cloudflare integration.
Use Cloudflare’s diagnostic tools to check for misconfigurations.Check Response Headers:
Confirm that HTTP headers, including cookies, don’t exceed Cloudflare’s 16KB limit.
Remove unnecessary or overly verbose headers to stay within limits.Optimize Firewall Rules:
Whitelist Cloudflare IP ranges to avoid unintended blocks.
Update firewall configurations to ensure proper communication between Cloudflare and the origin server.Server Performance:
Ensure the server isn’t overloaded or running out of resources, which can cause abrupt disconnections.
Power Up with Scrapfly
ScrapFly provides web scraping, screenshot, and extraction APIs for data collection at scale.
- Anti-bot protection bypass - scrape web pages without blocking!
- Rotating residential proxies - prevent IP address and geographic blocks.
- JavaScript rendering - scrape dynamic web pages through cloud browsers.
- Full browser automation - control browsers to scroll, input and click on objects.
- Format conversion - scrape as HTML, JSON, Text, or Markdown.
- Python and Typescript SDKs, as well as Scrapy and no-code tool integrations.

FAQ
Before we wrap up this article lets cover some frequently asked questions about the 520 error.
Is Error Code 520 a server or Cloudflare issue?
It is typically a server-side problem but is displayed by Cloudflare when it cannot interpret the server’s response.
Can retrying resolve Error Code 520?
Yes, retrying often resolves the issue, as 520 errors are frequently temporary.
Can oversized HTTP headers cause this error?
Yes, Cloudflare limits HTTP headers (including cookies) to 16KB. Exceeding this can trigger a 520 error.
Summary
In this guide, we’ve covered:
- The definition and common causes of Cloudflare error code 520, including server miscommunication, empty responses, and oversized headers.
- Practical solutions such as retrying requests, optimizing server configuration, and leveraging cached content.
- Tools like Scrapfly to help overcome server errors and maintain workflows efficiently.
By understanding error code 520 and its root causes, you can take proactive steps to resolve and prevent it.