How to Ignore cURL SSL Errors
Learn to handle SSL errors in cURL, including using self-signed certificates. Explore common issues, safe practices.
cURl is a viable tool for requesting and transferring data from web pages. However, an obstacle is often encountered: authentication. In this guide, we'll explain how to set cURL authorization for different types:
Let's get started!
The basic auth credentials method is one of the oldest methods for managing HTTP authentication. It requires entering basic credentials data, username and password:
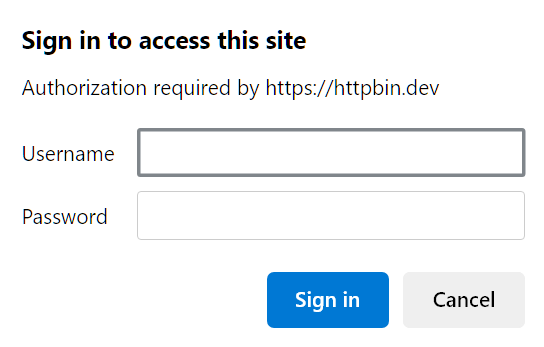
Authentication in the above image can be found at https://httpbin.dev/basic-auth/user/passwd . It requires entering the auth credentials before the request can proceed to the data.
To set basic authentication with cURL, we can use the --user or -u cURL options followed by the --basic option to mark it as basic auth:
curl --user user:passwd --basic https://httpbin.dev/basic-auth/user/passwd
The above cURL command will enter the credentials data (user and passwd) to authorize the HTTP request. Here is the response of the above cURL command:
{
"authorized": true,
"user": "user"
}
Bearer tokens are popular authentication methods for modern applications. They are tokens generated after the credentials are entered for the first time and used to pass authorization header for the requests to authenticate them.
If we go over the previous authentication endpoint on the browser and refresh the page, we'll find the authorization header used with the HTTP request headers:
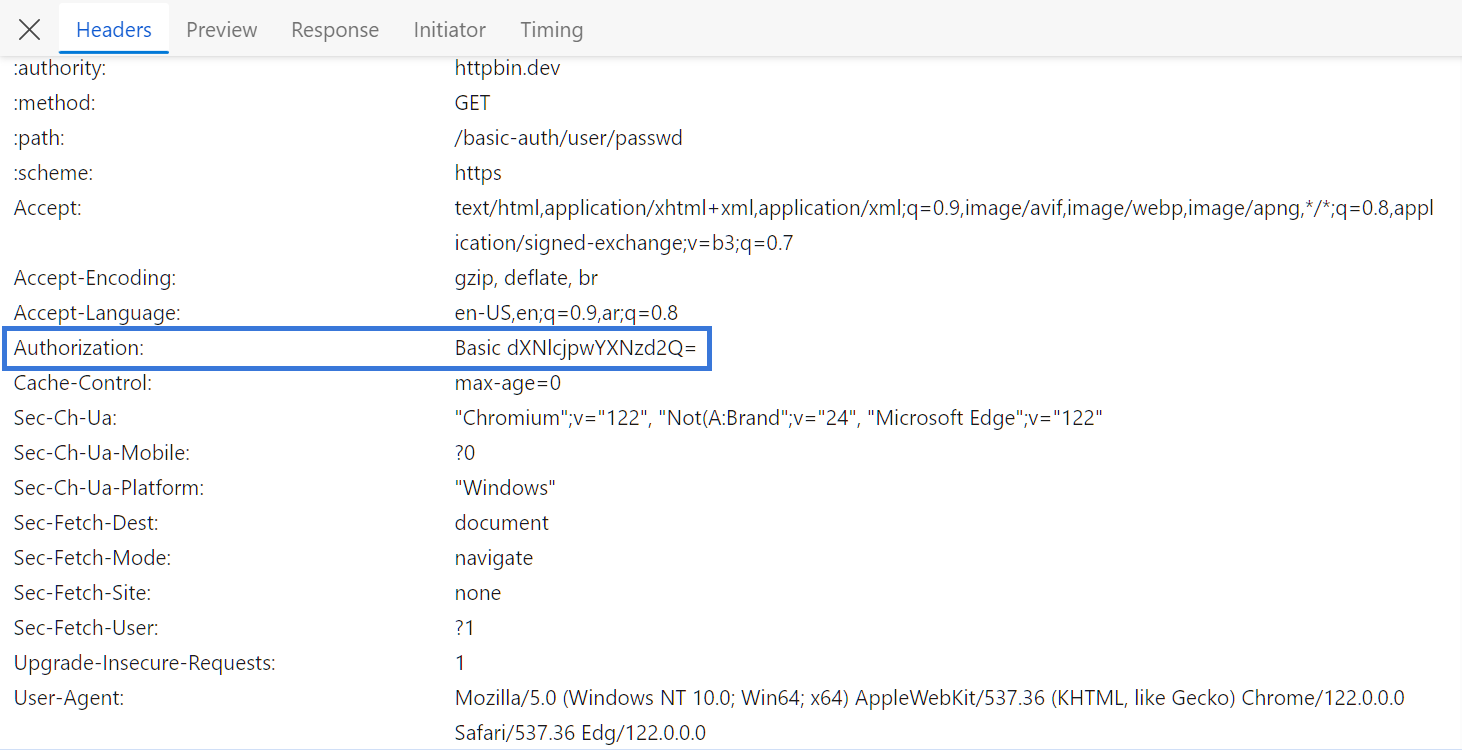
To set cURL Bearer authentication with cURL, we'll add the above Authorization header to the cURL command using the -H option:
To set Bearer authentication with cURL, we'll add the above Authorization header to cURL commands using the -H option:
curl -H "Authorization: Basic dXNlcjpwYXNzd2Q=" https://httpbin.dev/basic-auth/user/passwd
From the response, we can see that the cURL request was successfully authenticated:
{
"authorized": true,
"user": "user"
}
Another popular authentication method is using cookies, which function similarly to bearer tokens. After the credentials are validated successfully, a cookie value is created and saved to authorize future requests.
For this example, we'll use the login page on web-scraping.dev:
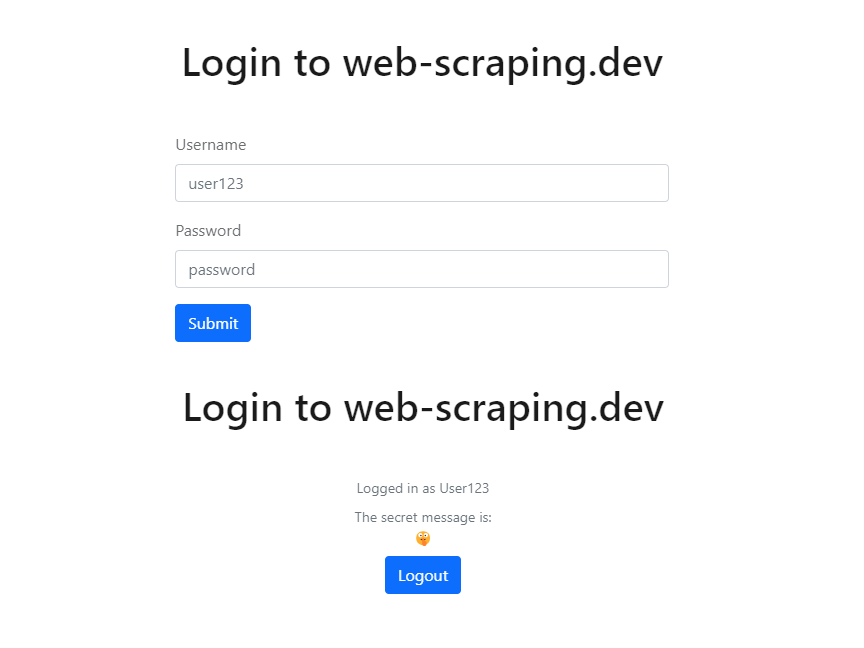
The above page uses a login form for authentication. If we take a look at the cookies for this domain, we'll find a cookie value for authentication:
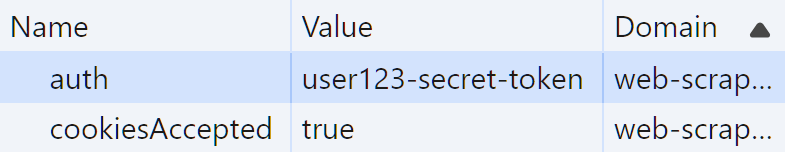
To handle cookie authentication with cURL, we'll pass this cookie value to the cURL command in either two ways:
-b cURL option.-H cURL option.curl -b "auth=user123-secret-token" https://web-scraping.dev/login
# or
curl -H "cookie: auth=user123-secret-token" https://web-scraping.dev/login
From the response, we can see that the cURL command was authenticated successfully:
<div class="container text-center">
<div class="form-text mb-2">Logged in as User123</div>
<div class="form-text mb-2">The secret message is:<div id="secret-message" class="fw-bold">🤫</div>
</div>
<a href="/api/logout"><button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary"> Logout </button> </a>
</div>
For further details on cURL, including configuring its commands and using it for web scraping, refer to our dedicated guide.
Explore sending and configuring cURL requests through a step-by-step guide. You will also explore advanced usages of cURL for web scraping, such as scraping dynamic pages and avoiding getting blocked.

This knowledgebase is provided by Scrapfly data APIs, check us out! 👇