When web scraping, it's often useful to monitor network requests. This enables retrieving crucial values found in response headers, body, or even cookies.
To better illustrate this, let's see what the request interception actually looks like using the below steps:
- Go to the login example on web-scraping.dev/login
- Open the devtools protocol by pressing the
F12 - Select the
Networktab - Fill in the login credentials and click login
After following the above steps, you will find each request event is captured, including its response details:
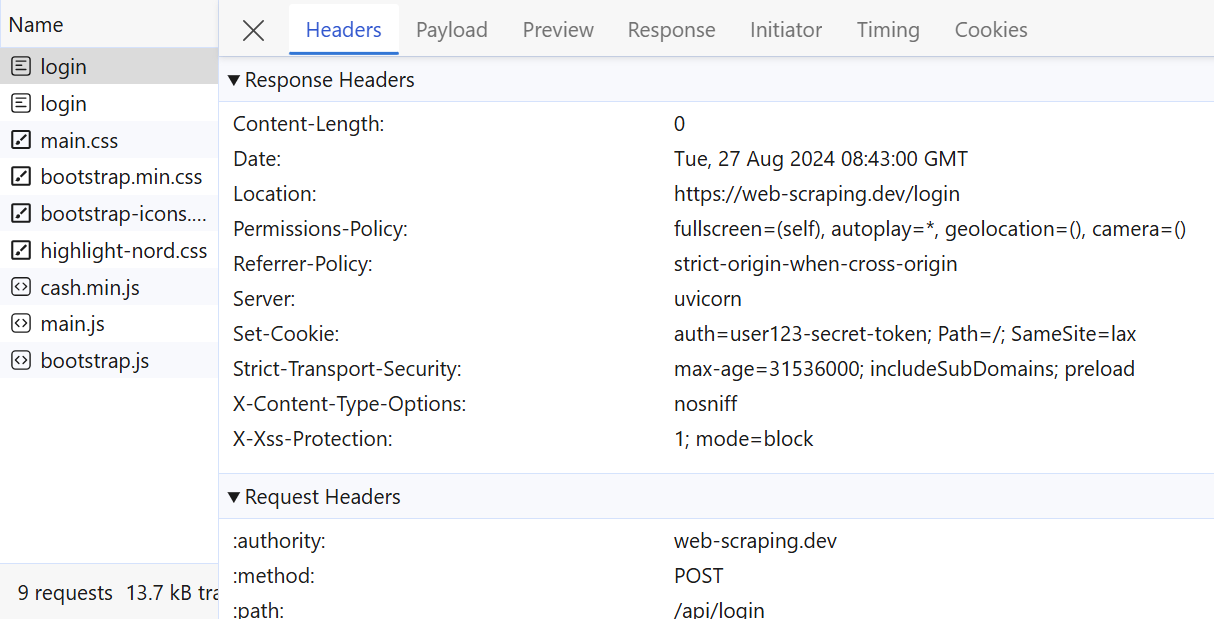
Above, we can observe the full details of the outgoing request. These details can be parsed to extract specific request-response values.
To allow Puppeteer get network requests and responses, we can use the page.on() method. This callback allows the headless browser to interept all network calls:
const puppeteer = require("puppeteer");
async function run() {
const browser = await puppeteer.launch();
const page = await browser.newPage();
// enable request interception
await page.setRequestInterception(true);
// capture background requests
page.on("request", (request) => {
console.log(request);
if (request.resourceType() === "xhr") {
console.log(request);
// we can block these requests with:
request.abort();
} else {
request.continue();
}
});
// capture background responses
page.on("response", (response) => {
console.log(response);
});
// request target web page
await page.goto("https://web-scraping.dev/");
await page.waitForSelector("footer", { visible: true });
await browser.close();
}
run();
Above, we allow Puppeteer capture background requests using the setRequestInterception method. Often, these background requests can contain important dynamic data. Blocking some requests can also reduce the bandwidth used while scraping, see our guide on blocking resources in Puppeteer for more.





